- ADD:Hongzhuang Road, East Town Industry Area, Yaoguan Town, Wujin District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, PR. China

- Mobile Phone:+86-15961181358
- Fax:+86-519-88700526
- E-mail:wk1358@dongchuan.cn
How Does A Sprocket And Chain Work?
Have already visited 4405/29/2025In industrial automation and material handling systems, the precise coordination between sprockets and conveyor chains lies at the core of power transmission. Whether it is the uniform operation of a food production line or the heavy-duty traction of mining machinery, their collaborative mechanism directly determines the efficiency and reliability of the equipment. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of how sprockets and chains work, revealing the engineering wisdom behind them in an accessible manner.
1. Core Mechanism of Power Transmission: From Rotational to Linear Motion
The Essence of Meshing Drive
Sprockets convert rotational motion into linear movement of the chain through precise meshing between their teeth and the rollers or links of the conveyor chain. During this process, the tension side (tight side) of the chain bears the pulling force, while the slack side maintains appropriate sag through gravity or tensioning devices to prevent derailment.

Efficiency Advantage of No-Slip Transmission
Unlike the elastic slip in belt drives, chain drives feature a larger meshing contact area and lower energy loss, achieving a transmission efficiency of up to 98%. This makes them particularly outstanding in scenarios requiring precise synchronization, such as packaging machinery.
Balance Between Speed and Load
The matching of sprocket teeth count and chain pitch is critical: fewer teeth increase impact, while a too-large pitch limits speed. Generally, the chain speed is recommended to be controlled within 12 m/s to balance dynamic load and stability.
2. Structural Design: Engineering Details of Sprockets and Conveyor Chains
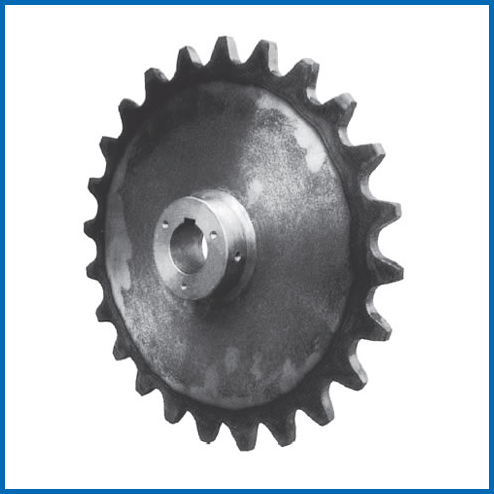
Tooth Profile and Material of Sprockets
Tooth Profile Optimization: Most sprockets adopt the "three-arc-one-line" tooth profile design (in line with ISO standards), reducing friction between rollers and tooth grooves and extending service life.
Material Selection: From Q235 carbon steel to 40Cr alloy steel, sprockets of different materials can adapt to high-temperature, corrosive, or heavy-load environments. For example, cast sprockets (ZG310-570) are commonly used in mining equipment, while carburized and quenched 20Cr material is suitable for high-impact scenarios.
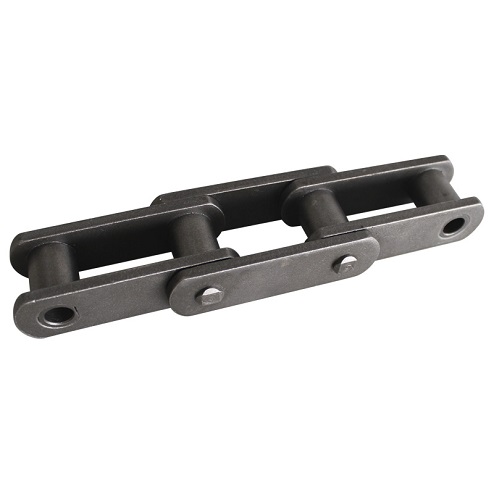
Diversified Forms of Conveyor Chains
Roller Chains: Composed of inner/outer link plates, pins, and rollers, these chains reduce friction with sprockets and are suitable for high-speed and light-load scenarios.
Multi-Row Chains: Double or triple-row designs enhance load-bearing capacity, commonly used in heavy-duty conveying systems in the metallurgical or building materials industry.

3. Performance Optimization: Matching Design and Maintenance Strategies
Transmission Ratio and Tooth Count Matching
The transmission ratio is recommended to be ≤8. The small sprocket should have ≥17 teeth to avoid impact, while the large sprocket's tooth count is dynamically adjusted according to the load. For example, small sprockets in food production lines typically have 25 teeth to balance efficiency and noise.
Lubrication and Wear Management
Lubrication Methods: Drip lubrication is suitable for low-speed scenarios, while oil bath systems are used in high-speed and high-load environments. Lack of lubrication can cause pin and bushing galling, shortening chain life.
Wear Detection: Regularly measure the chain pitch elongation rate (replace if exceeding 3%) and check whether sprocket tooth profiles are "hooked" due to wear.
Installation and Layout Key Points
Sprocket axes should be kept horizontal or at an inclination <45° to avoid poor meshing in vertical layouts. The tight side is usually arranged at the top to reduce the impact of slack side vibration on transmission.
4. Application Scenarios: Why Choose Chain Drives?
Industry Adaptability
Conveyor chains are the first choice in industries such as chemical engineering and automotive manufacturing due to their high-temperature resistance (up to 200°C) and pollution resistance. For example, in automotive welding workshops, stainless steel chains can withstand metal dust erosion.
Economy and Reliability
Low Maintenance Cost: Compared with gear drives, chain drives have lower manufacturing precision requirements, reducing maintenance costs by over 30%.
Long-Distance Transmission: Through multi-stage sprocket grouping, material conveying over tens of meters can be easily achieved without complex relay equipment.
Conclusion: Trust DONGCHUAN to Unlock New Heights of Transmission Efficiency
The precise coordination of sprockets and conveyor chains is the cornerstone of efficient industrial equipment operation. DONGCHUAN has deep expertise in the chain transmission field, providing end-to-end solutions from design optimization to customized production. Using CNC machining and heat treatment processes, we ensure perfect matching of every set of sprockets and chains. Choosing DONGCHUAN means not only selecting quality but also ensuring sustained productivity!
- Prev: No Content
- Next: What is a cast chain?





View More(Total0)Comment Lists